
When you’re knee-deep in a complex print job, the last thing you want is to spend hours sorting and organizing pages manually. That’s where collating, often called sorting, comes in—a feature that can save you time, hassle, and headaches. If you've ever felt overwhelmed trying to understand printing terms or functionalities, you’re in the right place. Today, we’re diving into what collate means in printing, why it's useful, and how to make the most of it with your printer.
At Strategic Technology Partners of Texas (STPT), we’ve been providing top-tier printers to hundreds of businesses for nearly 40 years. Our extensive experience means we know how printers work and how to utilize them to their full potential. This blog aims to share our expertise and help you harness the power of your printing technology.
By reading this article, you'll gain a clear understanding of:
- What collate means in printing.
- When and why you should use collating.
- How collating works and the technology behind it.
- Different types of collation and their best use cases.
- Step-by-step guide on how to collate on a printer.
- The role of print finishers in collating.
What Does Collate Mean in Printing?
Collating in printing involves grouping multi-page documents in a specific order or sequence. Each set of related documents is printed and grouped together before the next set starts. For instance, if you're printing a 10-page document and need 30 copies, collating ensures each complete set (pages 1-10) is grouped together before the next set begins. Many people call this process sorting, as it organizes the pages into the correct order.
Historically, collating was done by hand, which was labor-intensive and time-consuming. It wasn't until the late 1880s when Herman Hollerith developed a mechanical tabulator, that the process began to be automated. His innovations paved the way for modern mechanical collation, drastically reducing the time required for large sorting tasks.
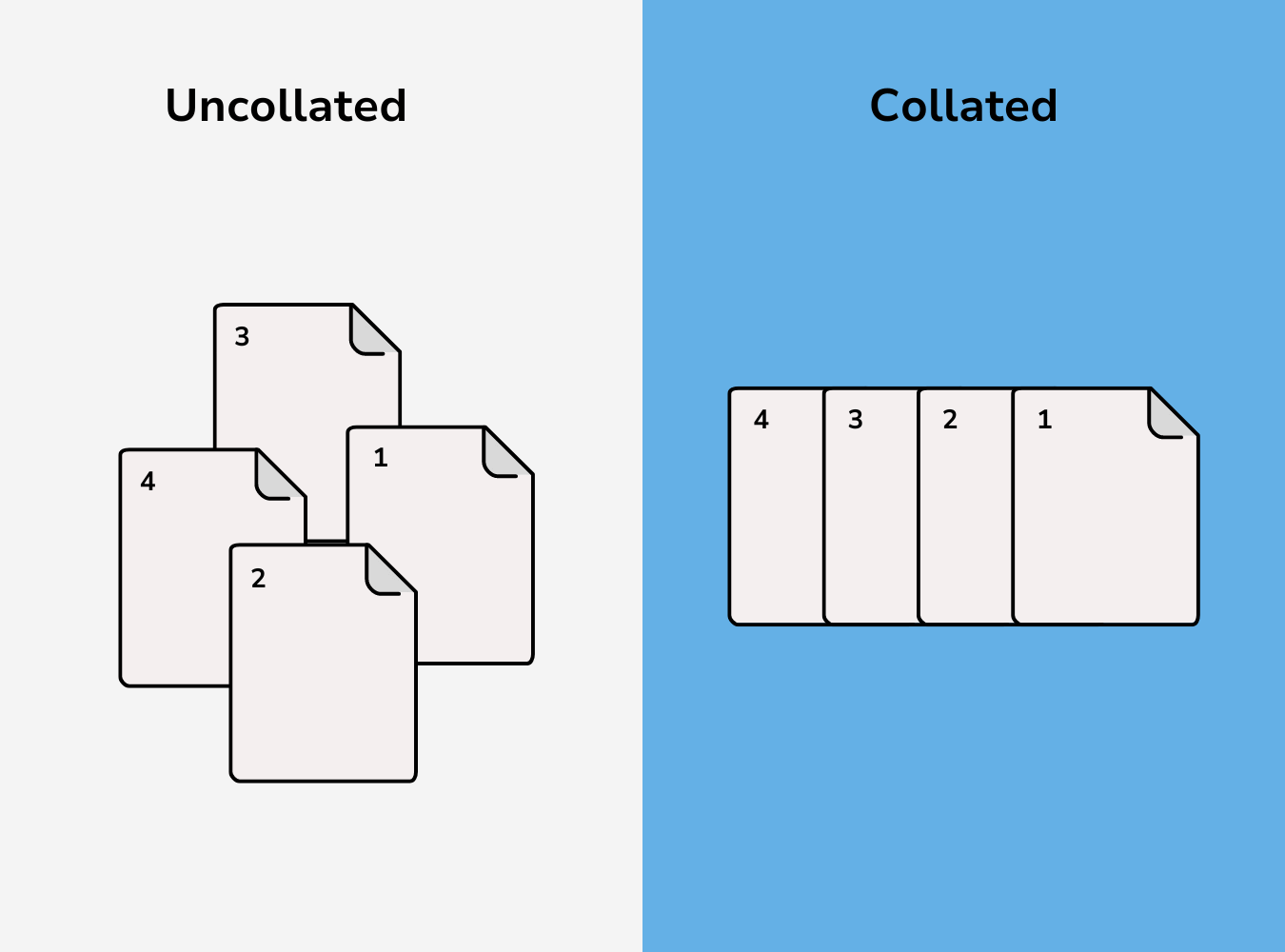
Why Collate? The Advantages and Use Cases
Efficiency and Convenience
Imagine you’re a teacher preparing worksheets for your class. Without collating, you would print all copies of page 1, then all copies of page 2, and so on. This process requires manual sorting, which is time-consuming and prone to errors. With collating, each complete set is printed in sequence and ready to distribute directly.
Professional Presentation
Collating makes your documents look neat and organized. Whether it's a report, manual, or a multi-page flyer, collating ensures everything is in the proper order, making it easier to read and more professional.
Time-Saving
One of the most significant advantages of collating is the time saved from manual sorting. Especially for large print jobs, collating can drastically cut down on preparation time, allowing you to focus on more important tasks.
How Does Collate Printing Work? The Technology Behind It
When you select the collate option for a multi-copy, multi-page print job, the printer will group the pages of each copy together before starting the next set. Printer collation uses advanced computer algorithms and hardware to arrange pages in the correct order for printing.
Modern printers have collating functions you can enable through the printer or your document application's print settings. This feature ensures that each set is printed in sequence before proceeding to the next.
To use Xerox as an example: Smaller printer units, especially those supporting only A4 paper size (8.5x11”), may require print finishers to handle collating. Larger, floor-standing units that support A3 size typically include collating features by default. Read about the difference between A3 and A4 printers here.
Different Types of Collate and Their Best Use Cases
There are different types of collating options, each suited for specific tasks:
1. Sequential Collating
This is the most common type of collating, where pages are grouped in order (1, 2, 3, etc.) for each set. Best for:
- Reports and manuals.
- Educational materials.
- Multi-page handouts.
2. Reverse Collating
Sometimes, you might need to collate in reverse order (10, 9, 8, etc.). This is useful when binding or stacking documents where the last page should be on top.
3. Custom Collating
For specialized projects, custom collating might be necessary. This involves specific sequencing or grouping of pages tailored to unique needs, such as legal documents or bespoke marketing materials.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Collate on a Printer
Enabling Collating on Your Printer:
Through Printer Settings:
- Access your printer's device management settings.
- Look for the collate option, which is usually found in the print settings menu.
- Enable collate and apply the settings.
Through Application Print Window:
- Open the document you wish to print.
- Go to the print dialog box (usually found under File > Print).
- Check the collate option, which is typically enabled by default.
- Confirm and start printing.
Tips for Effective Collating:
- Ensure your printer has enough paper and ink/toner.
- Double-check settings to avoid misprints.
- For large jobs, consider doing a test print to verify the sequence.
Why Use a Print Finisher When Collating?
If you work at a school or deal with a large number of documents every day, chances are you use a multifunction printer (MFP) with a print finisher. These perform the final printing process step and can automatically do tasks like staple and hole punch your documents.
Print finishers can handle complex collating tasks more efficiently and with greater precision than standard printers. They are ideal for high-volume print jobs, ensuring each document set is correctly organized and ready for immediate use. Complex print jobs requiring precise sequencing or mixed media benefit from the advanced capabilities of print finishers.
Considerations for Collating with Print Finishers
When using print finishers to collate, consider the following:
- Volume of Print Job: Ensure the finisher can handle the volume of your print job without requiring constant intervention.
- Document Type: Different finishers can handle different paper sizes, weights, and types. Ensure your finisher is compatible with your document requirements.
- Complexity of Collation: For more complex collation tasks, such as mixed media or custom sequences, ensure your finisher supports these advanced features.
- Speed and Efficiency: High-speed finishers can significantly reduce production time for large print jobs.
What Print Finishers Can Collate?
Many major printer brands offer print finishers with collating capabilities. Brands like Canon, Ricoh, HP, and Konica Minolta provide advanced finishers that can handle collating tasks efficiently. These finishers are typically part of larger multifunctional printer systems designed to produce high-volume and high-quality output.
All Xerox print finishers, for example, come with the collate option.
Discover More Printing Techniques
Understanding collating in printing can greatly improve your workflow, saving you time and ensuring your documents are professionally presented. Whether you’re a teacher, a business professional, or anyone with multi-page print needs, collating is a valuable feature.
At STPT, we’re committed to helping you make the most of your printing technology. Now that you know what collating is and how to use it, you’re better equipped to handle your print jobs efficiently.
Want to learn more about printing techniques? Check out our blog on the different types of print finishing options to enhance your documents. Click the image below to read more.
