
If you’ve ever looked at a custom phone case, a perfectly sculpted action figure, or even a prosthetic limb and thought, “How on earth did they make that?”—the answer is 3D printing.
This cutting-edge technology has come a long way from its sci-fi origins, and it’s no longer just for engineers and tech enthusiasts. Today, it’s even possible to 3D print a house!
When it comes to 3D printers, there are many different types to choose from. So, where should you begin?
As long-time print vendors (nearly 40 years, to be exact), our knowledge of printers is vast, and 3D printing is a technology that excites us.
In this article, we’ll give you a quick introduction into the world of 3D printers by breaking down the different types, how they work, and what they’re best suited for. By the end, you’ll know enough to impress your friends with your newfound knowledge—or at least make an informed decision if you’re considering diving into the world of 3D printing.
Curious about the evolution of print? Check out our blog on the history of the printing industry.
What is 3D Printing?
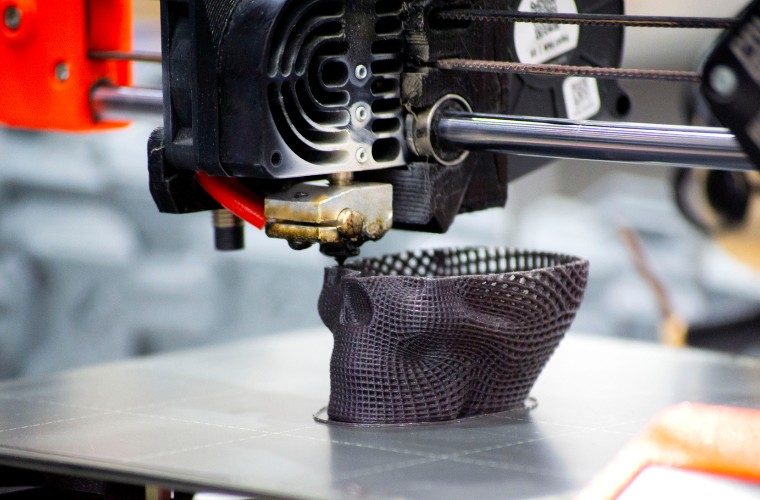
Let’s start with the basics: what is 3D printing? Also known as additive manufacturing, 3D printing creates objects by layering material on top of itself until the final shape emerges.
Unlike traditional manufacturing, which often involves cutting or carving material away, 3D printing is all about adding.
This unique process allows for incredible customization, minimal waste, and the ability to create complex designs that would be nearly impossible to produce using other methods. Whether you’re printing prototypes, spare parts, or even art, 3D printing is transforming industries like healthcare, automotive, education, and more.
So, why does it matter? Because the type of 3D printer you choose will directly impact what you can create. Let’s dive into the main types of 3D printers and what makes each one unique.
Types of 3D Printers
Not all 3D printers are the same. Each type uses a different technology, material, and process to achieve its results. Here are the main categories:
1. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
- How It Works: FDM printers melt a plastic filament and layer it to build the object.
- Materials Used: Common plastics like PLA and ABS.
- Applications: Prototyping, hobby projects, and educational purposes.
- Pros: Affordable, easy to use, and widely available.
- Cons: Lower precision and finish compared to other types.
FDM printers are perfect for beginners or anyone on a budget. Think of them as the entry-level model of the 3D printing world.
2. Stereolithography (SLA)
- How It Works: SLA printers use a laser to cure liquid resin into solid layers.
- Materials Used: Photopolymer resins.
- Applications: Dentistry, jewelry, and highly detailed models.
- Pros: High precision and smooth finishes.
- Cons: More expensive and requires post-processing.
If you’re looking for detailed, professional-quality results, SLA printers are your go-to. Just be ready for a little more maintenance.
3. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
- How It Works: SLS uses a laser to fuse powdered material layer by layer.
- Materials Used: Plastics, ceramics, and even metals.
- Applications: Industrial manufacturing, functional prototypes, and complex designs.
- Pros: Strong, durable parts with no support structures needed.
- Cons: High cost and industrial-grade equipment required.
SLS printers are the heavyweights of 3D printing—ideal for serious manufacturing.
4. Digital Light Processing (DLP)
- How It Works: Similar to SLA, but uses a digital projector instead of a laser.
- Materials Used: Liquid resins.
- Applications: Similar to SLA—dental models, intricate designs, and high-detail items.
- Pros: Faster than SLA with similar precision.
- Cons: Resins can be pricey.
Think of DLP as SLA’s slightly faster cousin.
5. Material Jetting
- How It Works: Material is sprayed layer by layer, like an inkjet printer.
- Materials Used: Photopolymers and waxes.
- Applications: Prototypes, medical models, and highly detailed parts.
- Pros: Extremely precise and allows for multi-material printing.
- Cons: Expensive and not widely available.
Material jetting is for those who need precision and versatility—if your budget allows.
How to Choose the Right 3D Printer
Feeling overwhelmed? Don’t worry—you’re not alone! Here are some tips to help you choose the right type of 3D printer:
- Determine Your Budget: Start with what you’re willing to spend.
- Consider Your Project Goals: Are you printing basic prototypes, intricate designs, or functional parts?
- Think About Materials: Different printers work with different materials—some are more affordable than others.
- Factor in Maintenance: SLA printers, for instance, require extra care compared to FDM models.
Future Trends in 3D Printing
What’s next for 3D printing? Some exciting trends include:
- Multi-Material Printing: Combining materials for more complex designs.
- Bioprinting: Printing tissue and organs for medical use.
- AI Integration: Smarter printers that optimize processes automatically.
As technology continues to evolve, 3D printing will only become more accessible and impactful.
Learn More About Printers
3D printing is no longer a niche technology—it’s shaping industries, sparking creativity, and solving real-world problems. Whether you’re a curious beginner or a business exploring innovative solutions, understanding the types of 3D printers is the first step to unlocking their potential.
At Strategic Technology Partners of Texas, we’re here to guide you on your printer knowledge journey, with nearly four decades of expertise and a commitment to staying at the forefront of printer technology.
Ready to learn more about printers? Explore our Learning Center, where we host articles, how-to guides, and general knowledge on all things printer-related. If you have any questions, reach out to us today—we’d love to help you on your printer journey!
